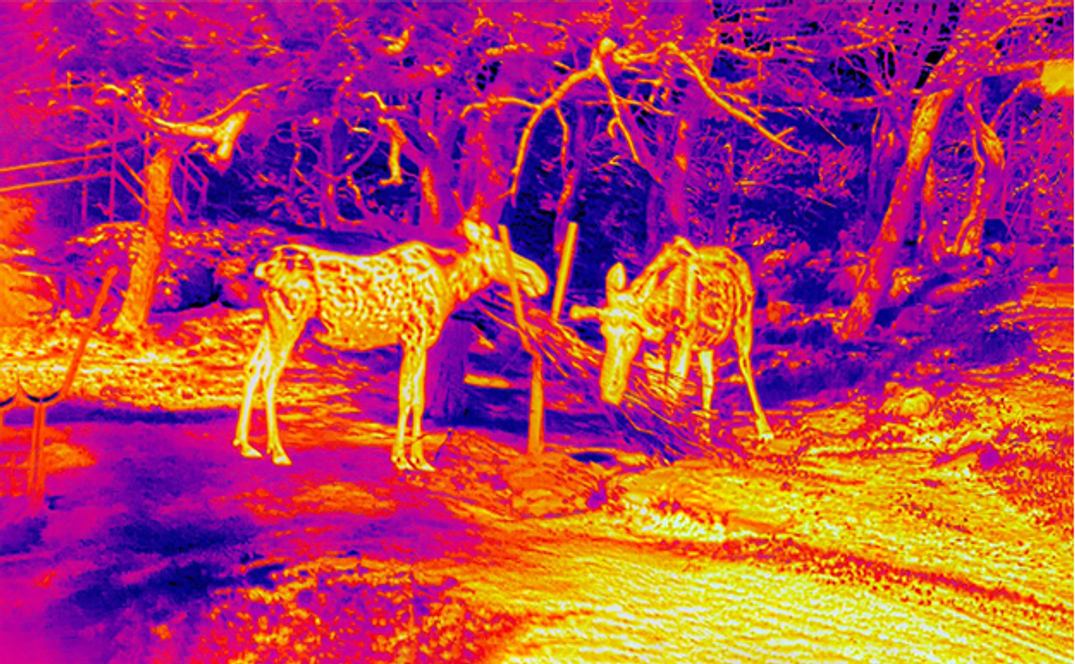
A thermal scope is basically an infrared camera with a reticle that’s designed to be mounted to a firearm platform; some thermal scopes also have integrated rangefinders and are richly outfitted with a variety of features that make it easier for hunters to ID and harvest their target quarry.
However, the world of thermal rifle scopes is distinct from that of more conventional optics, with some terms shared between them, and a number of terms that are distinct to thermal optics. These are some of the more critical ones that you need to be able to understand to know what you’re looking at in terms of features and capabilities.
Objective Lens
The objective lens of a thermal scope is the lens at the front of the scope. Unlike traditional optics, which rely on a larger objective lens to gather light and produce a higher quality image, thermal scopes utilize a thermal sensor. Also, the objective lenses of thermal scopes are made of germanium, not glass, which offers excellent heat transfer and low optical dispersion.
FOV (Field of View)
To put it as simply as possible, the field of view is how wide an image the operator can see, at a given distance, when looking through the scope. The wider the field of view (which is partially a product of the objective lens) the more the operator will be able to see downrange.
Base Magnification
The base magnification is the lowest fixed magnification setting of a thermal optic. If a fixed-magnification scope has a base magnification of 4x, that means the image in the scope will be 4x larger than the actual image appears to the naked eye. Some thermal scopes also offer variable magnification, which means that the user can increase the magnification setting to zoom in on the target.
Detection Range
A thermal scope’s detection range is the greatest possible distance that the scope can be used to effectively distinguish thermal signatures. As a general rule, the scope will be effective at ranges closer than the maximum range.
Refresh Rate
Like other electronics with video recording capabilities that produce images, thermal scopes produce a digital image on the display, viewed by the operator. The higher the refresh rate, the higher the frequency that the image is regenerated, and the less lag the operator will experience.
While standing still, it can be hard to detect a noticeable difference between thermal imaging scopes with similar refresh rates, but when scanning, scouting, or when viewing from a moving vehicle, the lag can become noticeable. To keep things simple, any scope with a refresh rate lower than 50 Hz should be avoided because it will produce a noticeable lag. A refresh rate between 50 and 60 Hz produces minimal lag with a few scopes in the 90 Hz range producing virtually no detectable lag, even with a moving target or from a moving platform.
Pixel Pitch
Pixel pitch is roughly the size of the pixels in a thermal sensor, alternatively, the distance between them. It is measured in micrometers, or μm, and the lower the number, the smaller each pixel is. Generally, a smaller pixel pitch is associated with a sharper image, but this is also tied to resolution. High quality sensors have a pixel pitch in the area of 12 μm, with most between 12 and 17 μm.
Sensor Resolution
The thermal camera core is the most critical part of any thermal sensor, and it is this core that has a specific resolution which will largely determine how sharp the image produced by the sensor is.
Holding all else equal, the higher the resolution, the sharper the image will be. High-end thermal scopes have resolutions as high as 1280x1280, while others on the more affordable end of the spectrum offer lower resolutions.
NETD
NETD, or “noise equivalent temperature differential,” is measured in millikelvin, or mK, and gives an indication of how sensitive the sensor is with respect to detecting a change in temperatures. The lower the NETD rating, the more sensitive the sensor is. This is critical in hot, muggy and high humidity conditions, as well as in circumstances where there isn’t a large difference in temperatures between different objects picked up by the sensor. The lower the NETD rating, the sharper the image will be. All in all, you want a thermal scope with a low NETD rating and a high resolution, which will produce a sharp and detailed image.
Eye Relief
Eye relief is the distance from your eye at which the scope must be placed on the receiver in order to produce a full, clear sight picture. The better the eye relief the further you can see the entire screen and keep your eye back from the scope preventing scope contact with your face for higher recoil rifles.
Display Type
There are two common display types in thermal scopes, which are AMOLED and OLED displays.
OLED displays are the more affordable of the two and generally produce a wider field of view. As for AMOLED displays, while they are more expensive, they usually have a faster refresh rate along with higher resolutions, producing clearer, sharper images. This often justifies the higher price point associated with them.
Display Resolution
Display resolution is the resolution the screen inside the scope (the screen you watch in the thermal) can produce. Not to be confused with the “Sensor Resolution”. Most scopes have a Display Resolution around 1024 x 768, but some higher end scopes and monocular’s are now coming with 2560 X 2560 resolutions. These higher resolution screens can enhance the image clarity of the sensor and also makes the overlaid information such as the reticle, icons, menus and information banners to be much clearer and easier to read at increased angles. It also allows for more finite adjustments to the reticle for more precise shooting since the reticle can be indexed in smaller increments.
Explore Thermal Scopes from the Top Brands at Dark Night Outdoors
While this compilation is far from comprehensive, if you understand the thermal optic terminology mentioned here, you will begin to acquire a working understanding of how to parse the details of model specifics and features. Shop our full collection of thermal scopes from top brands here, and if you have questions about specifications, get in touch with us.


